Capability Analysis in Process Improvement Explained
Capability analysis is a critical tool in process improvement, used to assess how well a process can meet specified requirements. By analyzing a process's ability to produce outputs within defined limits or tolerances, organizations can gain insight into its performance and stability. Capability analysis is integral to quality control, Lean Six Sigma, and continuous improvement initiatives, enabling businesses to reduce variability, minimize defects, and enhance customer satisfaction.
This article delves into the key concepts, methods, and applications of capability analysis in process improvement, highlighting its role in driving operational excellence.
Key Concepts in Capability Analysis
1. Process Capability
Process capability refers to the inherent variability of a process and its ability to meet specifications. A process is said to be capable if its natural variation, under stable conditions, consistently produces outputs within specification limits. Two key terms are used in process capability:
- Specification Limits: These include the Upper Specification Limit (USL) and Lower Specification Limit (LSL) defined by customer requirements.
- Control Limits: Limits based on statistical control of the process, typically ±3 standard deviations from the process mean.
2. Capability Indices
The capability of a process is quantitatively assessed using capability indices. These indices help in comparing the process performance against specified tolerance limits:
- Cp: The ratio of the specification width to the process width, showing whether the process is capable of producing within limits. It is calculated as:
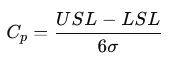 where σ\sigmaσ is the standard deviation of the process.
where σ\sigmaσ is the standard deviation of the process.- If Cp>1, the process is capable.
- If Cp<1, the process needs improvement.
- Cpk: Measures how centered the process is within its specification limits. It is the minimum of the process capability indices calculated for both the upper and lower sides:
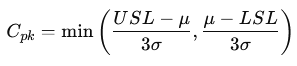
- If Cpk>1, the process is capable and well-centered.
- If Cpk<1, the process is off-center and may produce defects even if Cp > 1.
3. Process Performance Indices
In cases where the process is not in statistical control, process performance indices are used:
- Pp: Similar to Cp, but it measures the overall performance rather than just the process capability when the process is stable.
- Ppk: Analogous to Cpk but reflects actual process performance when instability is present.
Click Here to Join the Over 6000 Students Taking Highly Rated Courses in Manufacturing, Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Project Management, Engineering, Food Safety, Lean Six Sigma, Industrial Safety (HSE), Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, Product Development etc. on UDEMY.
Steps in Conducting Capability Analysis
1. Define Process Objectives and Specifications
The first step in any capability analysis is to clearly define the objectives of the process improvement effort and establish the specification limits (USL and LSL). Understanding customer requirements or regulatory standards is key to setting these limits.
2. Gather Process Data
Collecting data on the process output is essential for assessing its performance. This data should be gathered under normal operating conditions to reflect the true behavior of the process.
3. Evaluate Process Stability
Before conducting capability analysis, the process must be evaluated for statistical control using control charts. If the process is unstable (out of control), any capability analysis may provide misleading results. If necessary, take steps to stabilize the process by addressing assignable causes of variation.
4. Calculate Capability Indices
Once the process is stable, capability indices (Cp and Cpk) are calculated to determine how well the process meets its specifications. Use appropriate statistical software or manual calculations.
5. Interpret Results and Identify Improvement Areas
The final step is to interpret the results. If the process capability indices indicate that the process is not capable, improvement initiatives should be designed to reduce variability and center the process within the specification limits. Common strategies include:
- Reducing sources of variation (using Lean Six Sigma tools such as DMAIC).
- Adjusting the process mean to bring it closer to target specifications.
- Enhancing process control mechanisms to maintain consistency.
Click Here to Join the Over 6000 Students Taking Highly Rated Courses in Manufacturing, Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Project Management, Engineering, Food Safety, Lean Six Sigma, Industrial Safety (HSE), Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, Product Development etc. on UDEMY.
Applications of Capability Analysis in Process Improvement
Capability analysis is widely used in various industries to improve processes and enhance quality. Below are key areas where it plays a crucial role:
1. Manufacturing Process Optimization
In manufacturing, ensuring that processes produce parts or products within specifications is critical to maintaining high-quality output. Capability analysis allows manufacturers to detect when processes are deviating from target and take corrective action to prevent defects. This reduces scrap rates, rework, and associated costs.
2. Lean Six Sigma and Continuous Improvement
Capability analysis is a fundamental tool in Lean Six Sigma methodologies, especially within the Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control (DMAIC) framework. It helps in the "Measure" and "Analyze" phases, where the performance of a process is assessed against customer requirements, and the scope for improvement is identified.
3. Compliance with Industry Standards
Many industries, including automotive, aerospace, and pharmaceuticals, have stringent quality standards. Capability analysis helps organizations demonstrate compliance with these standards by ensuring that critical processes consistently meet defined tolerances.
4. Service Industry Applications
While capability analysis is commonly associated with manufacturing, it can also be applied in service industries. For example, in healthcare, it can be used to measure the capability of a hospital's process in maintaining treatment times within acceptable limits. In finance, capability analysis helps assess the performance of transaction processing systems against service-level agreements (SLAs).
Click Here to Join the Over 6000 Students Taking Highly Rated Courses in Manufacturing, Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Project Management, Engineering, Food Safety, Lean Six Sigma, Industrial Safety (HSE), Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, Product Development etc. on UDEMY.
Benefits of Capability Analysis
1. Reduced Variability
By identifying and minimizing the causes of process variability, capability analysis leads to more consistent output, reducing the chances of defects and rework.
2. Improved Customer Satisfaction
Meeting customer specifications consistently ensures higher product or service quality, directly leading to increased customer satisfaction.
3. Data-Driven Decision Making
Capability analysis provides organizations with concrete, data-backed insights into their processes, enabling more informed decision-making regarding improvements and investments.
4. Cost Savings
Processes that consistently operate within specification limits tend to have lower costs due to fewer defects, less rework, and minimized waste.
Conclusion
Capability analysis is a powerful tool that provides insights into how well a process performs relative to specified limits. By assessing and improving process capability, organizations can achieve significant gains in quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Whether applied in manufacturing, service industries, or compliance efforts, capability analysis plays a crucial role in any continuous improvement initiative, making it an indispensable part of modern process optimization strategies.
By leveraging the insights from capability analysis, organizations can ensure that their processes are not only efficient but also aligned with their customers' expectations, fostering a culture of quality and operational excellence.
Top 50 Courses to Enhance your Skills Today!
1. ISO MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS IMPLEMENTATION & INTERNAL AUDITOR COURSES
- Integrated Management Systems (IMS) Implementation Course
- FSSC 22000 Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- ISO 22000 Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- ISO 22000 (HACCP, PRPs, oPRPs and CCPs) for Food Safety
- Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) Training Course
- ISO 9001 (QMS) Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- ISO 14001 (EMS) Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- ISO 45001 (OH&SMS) Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- Food Fraud Mitigation & Defense Certification Course
2. ISO LEAD AUDITOR COURSES
- ISO 50001 Energy Management Systems (EnMS) Lead Auditor Course
- ISO 22000 Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS) Lead Auditor Course
- ISO 14001 Environmental Management Systems (EMS) Lead Auditor Certification Course
- ISO 45001 Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OH&MS) Lead Auditor Certification Course
- ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems (QMS) Lead Auditor Course
3. MANUFACTURING, QUALITY, PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT, OPERATIONS & SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
- ISO/IEC 17025 – Laboratory Management Systems Certification
- Essentials of Engineering Project Management
- Construction Project Management
- Essentials of Contract Management
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
- Laboratory Management Systems (LMS) Essentials
- Certified Manager of Quality & Process Excellence
- Essentials of Facility Management
- Agile Project Management
- Engineering Codes, Standards and Specifications
- Industrial Process Safety
- Fundamentals of Risk Management
- Industry 4.0: Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
- Manufacturing Operations Management Certification Course
- Total Quality Management (TQM) Certification Course
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) MasterClass
- Certified Lean Management Professional™ (CLMP™)
- Six Sigma for Business and Manufacturing Process Improvement
- Product Management Certification Course
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Data Analysis Course
- Quality Assurance for Business and Operational Excellence
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Certification Course
- Essentials of Facility Management
- Agile Project Management
- Engineering Codes, Standards and Specifications