Comprehensive Guide to Mandatory Documents for Integrated ISO Management Systems Implementation
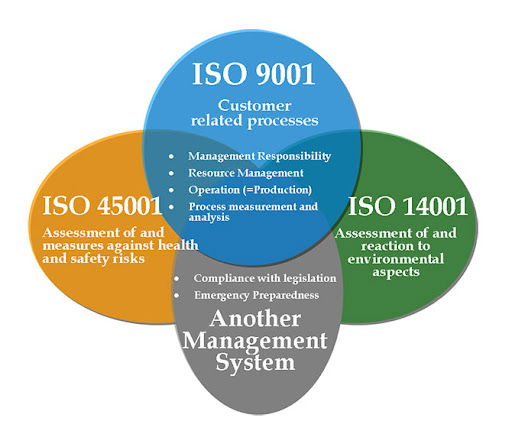
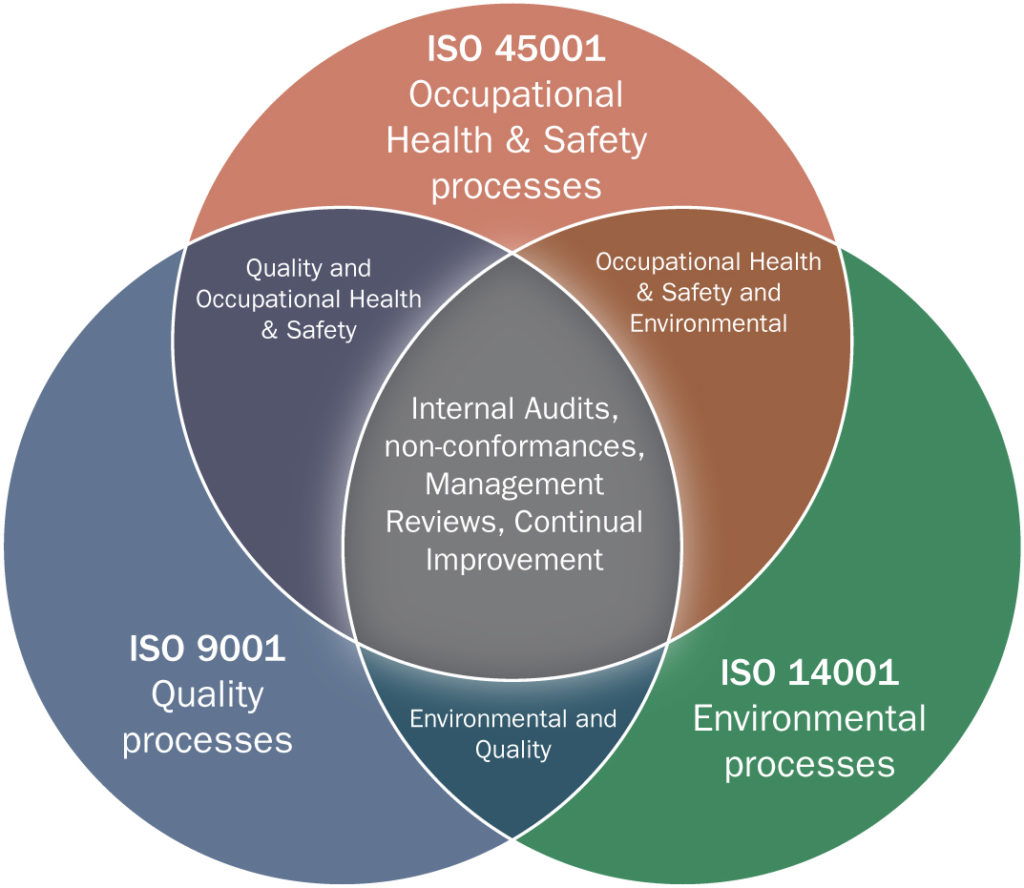
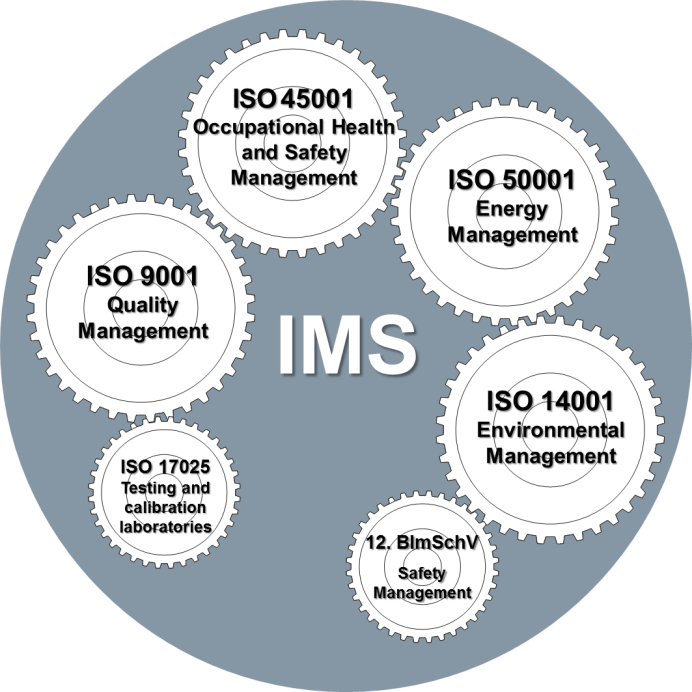
Implementing an Integrated ISO Management System (IMS) is a strategic move that can enhance organizational efficiency, ensure compliance, and foster continuous improvement. An IMS typically combines multiple ISO standards, such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety Management), into a cohesive framework. To effectively implement an IMS, certain mandatory documents are required to ensure the system's success and compliance with relevant standards.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to the mandatory documents necessary for Integrated ISO Management Systems implementation.
1. Integrated Management System (IMS) Manual
The IMS Manual is the cornerstone document that outlines the scope, structure, and key elements of the Integrated Management System. It provides an overview of how the organization integrates the various ISO standards and describes the relationships between them.
- Scope and Objectives: Defines the scope of the IMS, including the standards covered and the boundaries of the system.
- IMS Policy: Outlines the organization's commitment to quality, environmental, and occupational health and safety management.
- Process Descriptions: Provides a high-level description of key processes and their interactions within the IMS.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Clarifies the roles and responsibilities for maintaining and improving the IMS.
Click Here to Download Integrated Management Systems Implementation Kit
2. IMS Policy
The IMS Policy is a critical document that communicates the organization’s commitment to meeting the requirements of the integrated standards. It should be:
- Documented: Clearly written and accessible to all employees.
- Communicated: Regularly communicated within the organization and to interested parties.
- Reviewed: Periodically reviewed to ensure its continued suitability and effectiveness.
3. Risk and Opportunity Assessment
This document outlines the approach to identifying, assessing, and managing risks and opportunities related to the IMS. It should include:
- Risk Identification: Processes for identifying risks that could impact the IMS objectives.
- Risk Analysis: Methods for analyzing the likelihood and impact of identified risks.
- Risk Mitigation: Strategies for mitigating significant risks.
- Opportunity Identification: Identifying opportunities for improvement and optimization within the IMS.
4. Legal and Other Requirements Register
An IMS must comply with all relevant legal and regulatory requirements. This document should:
- Identify Applicable Laws and Regulations: A comprehensive list of legal and regulatory requirements relevant to the organization’s activities.
- Compliance Obligations: Methods for monitoring compliance and ensuring that all legal requirements are met.
- Updates: Procedures for keeping the register up to date with changes in legislation.
Click Here to Download Integrated Management Systems Implementation Kit
5. IMS Objectives and Targets
Setting objectives and targets is essential for driving continual improvement within the IMS. This document should include:
- Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound (SMART) Objectives: Clear objectives aligned with the IMS policy.
- Action Plans: Detailed plans for achieving the set objectives, including timelines and responsible persons.
- Monitoring and Review: Methods for tracking progress towards objectives and reviewing their effectiveness.
6. Process Documentation and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Process documentation and SOPs ensure consistency in how activities are carried out across the organization. This documentation should:
- Describe Key Processes: Detailed descriptions of key processes within the IMS.
- Define Roles and Responsibilities: Clear assignments of who is responsible for each process.
- Include Work Instructions: Step-by-step instructions for carrying out tasks to ensure compliance with the IMS.
7. Control of Documents and Records
Document control is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the IMS. This includes:
- Document Control Procedures: Guidelines for creating, reviewing, approving, and distributing documents.
- Record Control Procedures: Methods for identifying, storing, protecting, and retrieving records.
- Retention and Disposal: Policies for retaining records for a specified period and safely disposing of them when no longer needed.
8. Internal Audit Program and Reports
Internal audits are essential for verifying the effectiveness of the IMS. Documentation should include:
- Audit Schedule: A planned schedule for conducting internal audits.
- Audit Criteria and Scope: The standards and criteria against which the audit will be conducted.
- Audit Reports: Detailed findings from audits, including non-conformities and opportunities for improvement.
- Follow-up Actions: Procedures for addressing audit findings and verifying the implementation of corrective actions.
Click Here to Download Integrated Management Systems Implementation Kit
9. Management Review Records
Regular management reviews ensure the IMS remains effective and aligned with the organization’s strategic direction. This documentation should include:
- Review Agenda: Key topics to be discussed during the management review, such as performance, audit results, and improvement opportunities.
- Minutes of Meetings: Records of decisions made during the management review.
- Action Items: Follow-up actions resulting from the management review.
10. Non-Conformity and Corrective Action Records
Managing non-conformities and implementing corrective actions is crucial for continual improvement. Documentation should include:
- Non-Conformity Reports: Detailed records of non-conformities identified within the IMS.
- Root Cause Analysis: Methods used to determine the underlying causes of non-conformities.
- Corrective Action Plans: Strategies for addressing non-conformities and preventing their recurrence.
- Verification Records: Evidence that corrective actions have been effectively implemented.
11. Training and Competence Records
Ensuring that employees are competent and adequately trained is fundamental to the success of an IMS. Documentation should include:
- Training Needs Analysis: Identifying the training needs of employees related to the IMS.
- Training Records: Documentation of training provided, including dates, participants, and topics covered.
- Competence Assessment: Methods for assessing the competence of employees in performing their roles within the IMS.
12. Emergency Preparedness and Response Plan
Preparedness for emergencies is a critical component of an IMS. This document should:
- Identify Potential Emergencies: List potential emergencies relevant to the organization’s operations.
- Response Procedures: Detailed procedures for responding to identified emergencies.
- Communication Plans: Methods for communicating during an emergency, both internally and externally.
- Training and Drills: Records of emergency response training and drills conducted.
Click Here to Download Integrated Management Systems Implementation Kit
13. Environmental Aspects and Impacts Register
For organizations integrating ISO 14001, managing environmental aspects is essential. This document should include:
- Identification of Environmental Aspects: Processes for identifying activities, products, or services that interact with the environment.
- Impact Assessment: Methods for assessing the significance of environmental impacts.
- Control Measures: Strategies for managing significant environmental aspects to minimize impacts.
14. Health and Safety Risk Assessment
For ISO 45001 integration, a robust health and safety risk assessment is required. This document should include:
- Hazard Identification: Processes for identifying workplace hazards.
- Risk Evaluation: Methods for evaluating the risks associated with identified hazards.
- Control Measures: Strategies for mitigating health and safety risks.
- Monitoring and Review: Procedures for regularly reviewing risk assessments and control measures.
15. Supplier Evaluation and Approval Records
Managing suppliers is crucial to maintaining the integrity of the IMS. Documentation should include:
- Supplier Evaluation Criteria: Standards used to evaluate and select suppliers.
- Approval Records: Documentation of approved suppliers and their evaluation results.
- Performance Monitoring: Records of ongoing supplier performance reviews.
Conclusion
The successful implementation of an Integrated ISO Management System requires careful planning, execution, and documentation. The mandatory documents outlined in this guide form the backbone of the IMS, ensuring that the system is robust, compliant, and capable of driving continuous improvement. By maintaining these documents, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to quality, environmental stewardship, and occupational health and safety, while also positioning themselves for sustainable success.
Click HERE to download or any of the following documents:
ISO/IEC 17025 Laboratory Management System Implementation Kit
HACCP Implementation Kit
ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems (QMS) Implementation
ISO 22000 Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS) Implementation
Food Safety Systems Certification (FSSC) 22000 v5 Implementation
ISO 14001 Environmental Management Systems (EMS) Implementation
ISO 45001 Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OH&SMS) Implementation
ISO 50001 Energy Management Systems (EnMS) Implementation
Integrated Management Systems (IMS) Implementation
Production, Quality Control / Equipment Maintenance Kit
Lean Six Sigma
Lean Management/Manufacturing
Six Sigma Kit
Supplier Quality and Compliance Management (SQCM) Kit
Risk Management
Industrial Health, Safety & Environmental Management (HSE) Kit
Process Manuals