Comprehensive Guide to Rolled Throughput Yield (RTY)
Rolled Throughput Yield (RTY) is a key performance metric used in Lean Six Sigma and process improvement initiatives to assess the overall quality of a production process. It measures the probability that a unit will pass through a series of production steps without defects or rework. RTY is crucial for understanding the cumulative impact of individual process steps on the final yield and helps organizations pinpoint inefficiencies, reduce waste, and improve quality.
This article covers the definition of RTY, how it is calculated, its importance in continuous improvement, and strategies for its improvement.
What is Rolled Throughput Yield (RTY)?
RTY reflects the likelihood that a product or service can move through all stages of a process defect-free. Unlike traditional yield measures that may account for rework, RTY provides a purer measure by considering only the first-pass yield (the percentage of units passing through without defects on the first attempt). It helps quantify the hidden costs associated with quality issues like rework, scrap, or defects.
Click Here to Join the Over 6000 Students Taking Highly Rated Courses in Manufacturing, Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Project Management, Engineering, Food Safety, Lean Six Sigma, Industrial Safety (HSE), Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, Product Development etc. on UDEMY.
Example of Traditional Yield vs. Rolled Throughput Yield
Consider a manufacturing process with three sequential steps. Each step has the following individual yields (first-pass yields):
- Step 1: 95% yield (95 out of 100 units are defect-free)
- Step 2: 90% yield (90 out of 100 units pass without defects)
- Step 3: 85% yield (85 out of 100 units are defect-free)
In this scenario, the traditional yield for each step might look at the number of units corrected or reworked and consider that all the final products meet quality standards.
RTY, on the other hand, is calculated by multiplying the yields of each step:
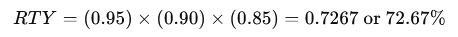
Thus, the overall process has an RTY of 72.67%, indicating that only 72.67% of the units pass through the entire process without any defects or rework, even though each individual process step may appear to perform well on its own.
Importance of RTY
- Identifying Hidden Defects: RTY reveals defects that are hidden by rework, scrap, and inspection stages. Even though traditional yield may look acceptable, RTY will show a much lower rate if rework or defect rates are high.
- Optimizing Process Performance: By breaking down a process into individual steps, RTY helps organizations understand how each step affects the overall quality. This makes it easier to target problem areas and improve process efficiency.
- Cost Reduction: Rework, waste, and defects incur hidden costs in materials, time, and labor. RTY highlights these inefficiencies, enabling companies to streamline processes, reduce unnecessary costs, and improve profit margins.
- Customer Satisfaction: A higher RTY indicates fewer defects and rework, resulting in higher-quality products. This leads to increased customer satisfaction as the likelihood of defective products reaching customers decreases.
Click Here to Join the Over 6000 Students Taking Highly Rated Courses in Manufacturing, Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Project Management, Engineering, Food Safety, Lean Six Sigma, Industrial Safety (HSE), Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, Product Development etc. on UDEMY.
How to Calculate RTY
To calculate RTY, follow these steps:
- Determine the First-Pass Yield for Each Step:
- For each step in the process, calculate the percentage of units that pass through defect-free on the first attempt. This is the First-Pass Yield (FPY) or Throughput Yield for that step.

- Multiply the First-Pass Yields: Multiply the FPYs of all the steps in the process to calculate the overall
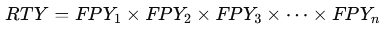 Where FPY1, FPY2 etc., are the yields of the individual steps in the process.
Where FPY1, FPY2 etc., are the yields of the individual steps in the process. - Interpret the Result: The resulting RTY will be a value between 0 and 1 (or 0% and 100%). A higher RTY means that a larger percentage of units pass through the entire process without any defects.
Example Calculation
Let's consider a simple three-step process:
- Step 1: 90 units out of 100 are defect-free → FPY = 90%
- Step 2: 80 units out of 100 are defect-free → FPY = 80%
- Step 3: 85 units out of 100 are defect-free → FPY = 85%
The RTY is calculated as:
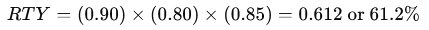
This indicates that only 61.2% of units pass through all three steps without defects or rework.
Click Here to Join the Over 6000 Students Taking Highly Rated Courses in Manufacturing, Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Project Management, Engineering, Food Safety, Lean Six Sigma, Industrial Safety (HSE), Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, Product Development etc. on UDEMY.
Improving RTY
Improving RTY requires focusing on process optimization at each step. Here are strategies to improve RTY:
- Reduce Variability: Implement statistical process control (SPC) to monitor and control process variability, reducing defects at each step.
- Standardize Work: Use standardized operating procedures (SOPs) to ensure consistency in production, which reduces the likelihood of defects.
- Identify and Eliminate Root Causes of Defects: Perform root cause analysis (RCA) using methods like 5 Whys or fishbone diagrams to pinpoint the causes of defects and implement corrective actions.
- Continuous Training and Development: Ensure that employees are properly trained and equipped to perform their tasks without introducing variability or errors.
- Automation and Error-Proofing (Poka-Yoke): Where possible, automate repetitive tasks and implement error-proofing mechanisms to prevent defects from occurring.
- Lean Six Sigma Tools: Use Six Sigma techniques such as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to systematically identify and remove defects from the process. Lean tools like Kaizen and 5S can help in streamlining processes and improving yield.
Monitoring and Reporting RTY
Regular monitoring of RTY is critical for maintaining and improving process performance. Organizations can integrate RTY into key performance indicators (KPIs) for process improvement. Visual management tools such as dashboards can help track RTY trends over time and ensure that process improvements are sustained.
Click Here to Join the Over 6000 Students Taking Highly Rated Courses in Manufacturing, Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Project Management, Engineering, Food Safety, Lean Six Sigma, Industrial Safety (HSE), Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, Product Development etc. on UDEMY.
RTY in Service Industries
Though RTY is more commonly associated with manufacturing, it can also be applied in service industries. For example, in a multi-step customer service process, RTY can be used to measure how many cases are resolved correctly the first time at each stage, without requiring rework or additional steps.
Conclusion
Rolled Throughput Yield (RTY) is a powerful metric that provides deeper insights into the quality and efficiency of a production process. By focusing on first-pass yields and avoiding the masking effect of rework or scrap, RTY helps businesses identify and address inefficiencies that traditional yield measures may overlook. By improving RTY, companies can reduce costs, enhance product quality, and increase customer satisfaction, all while driving continuous improvement initiatives.
Effective use of RTY as part of a comprehensive Lean Six Sigma approach can significantly improve operational performance and help an organization remain competitive in today's demanding market.
Top 50 Courses to Enhance your Skills Today!
1. ISO MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS IMPLEMENTATION & INTERNAL AUDITOR COURSES
- Integrated Management Systems (IMS) Implementation Course
- FSSC 22000 Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- ISO 22000 Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- ISO 22000 (HACCP, PRPs, oPRPs and CCPs) for Food Safety
- Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) Training Course
- ISO 9001 (QMS) Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- ISO 14001 (EMS) Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- ISO 45001 (OH&SMS) Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- Food Fraud Mitigation & Defense Certification Course
2. ISO LEAD AUDITOR COURSES
- ISO 50001 Energy Management Systems (EnMS) Lead Auditor Course
- ISO 22000 Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS) Lead Auditor Course
- ISO 14001 Environmental Management Systems (EMS) Lead Auditor Certification Course
- ISO 45001 Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OH&MS) Lead Auditor Certification Course
- ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems (QMS) Lead Auditor Course
3. MANUFACTURING, QUALITY, PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT, OPERATIONS & SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
- ISO/IEC 17025 – Laboratory Management Systems Certification
- Essentials of Engineering Project Management
- Construction Project Management
- Essentials of Contract Management
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
- Laboratory Management Systems (LMS) Essentials
- Certified Manager of Quality & Process Excellence
- Essentials of Facility Management
- Agile Project Management
- Engineering Codes, Standards and Specifications
- Industrial Process Safety
- Fundamentals of Risk Management
- Industry 4.0: Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
- Manufacturing Operations Management Certification Course
- Total Quality Management (TQM) Certification Course
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) MasterClass
- Certified Lean Management Professional™ (CLMP™)
- Six Sigma for Business and Manufacturing Process Improvement
- Product Management Certification Course
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Data Analysis Course
- Quality Assurance for Business and Operational Excellence
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Certification Course
- Essentials of Facility Management
- Agile Project Management
- Engineering Codes, Standards and Specifications