ऑडिट साक्षात्कार बढ़ाना: प्रभावशीलता के लिए तकनीक और उपकरण
Audit interviews are pivotal components of the auditing process, serving as opportunities for auditors to gather crucial information, clarify doubts, and assess the effectiveness of internal controls. Conducting effective audit interviews requires a combination of techniques and tools aimed at fostering communication, obtaining accurate insights, and ensuring the audit objectives are met.
In this article, we delve into various strategies and tools that auditors can employ to enhance the effectiveness of their audit interviews.
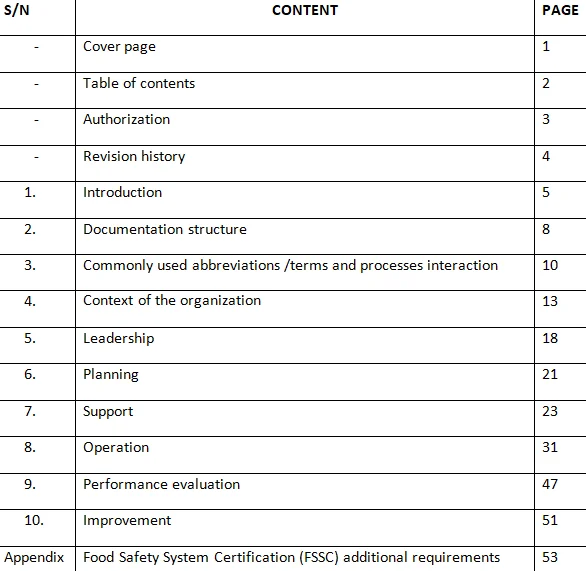
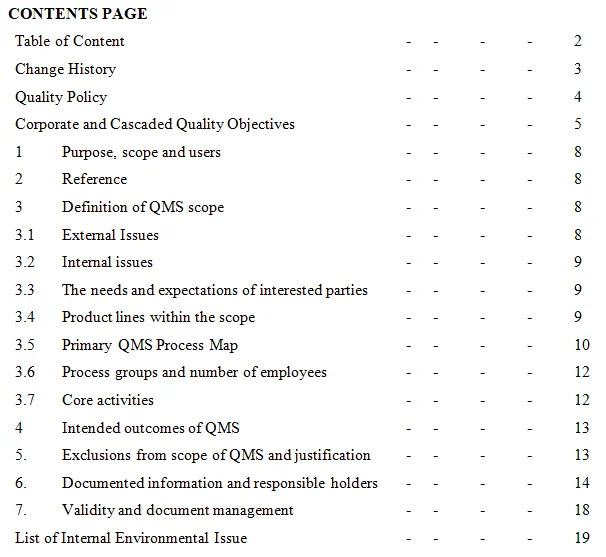
Click Here to Download Readymade Editable Toolkits & Templates on Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Lean Six Sigma, Risk Management, Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, HSSE, Project Management etc.
Techniques for Effective Audit Interviews
1. Establishing Rapport
Building a rapport with interviewees is essential for fostering an environment of trust and openness. Auditors should begin interviews with a friendly demeanor, actively listen to responses, and demonstrate empathy towards interviewees' concerns. Establishing rapport helps in eliciting candid responses and encourages interviewees to share pertinent information willingly.
2. Active Listening
Active listening involves attentively processing and comprehending the information provided by interviewees. Auditors should focus on the speaker, maintain eye contact, and avoid interrupting. Paraphrasing and summarizing key points during the conversation demonstrate understanding and facilitate clarification of complex concepts.
3. Open-ended Questions
Utilizing open-ended questions encourages interviewees to provide detailed responses, offering valuable insights into processes, controls, and potential risks. Open-ended questions typically begin with "what," "how," or "why," prompting interviewees to elaborate on their experiences and perspectives.
Click Here to Download Readymade Editable Toolkits & Templates on Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Lean Six Sigma, Risk Management, Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, HSSE, Project Management etc.
4. Probing
Probing involves delving deeper into responses to extract additional information or clarify ambiguities. Auditors should employ probing techniques such as asking for examples, seeking clarification on vague statements, and exploring inconsistencies. Effective probing aids in uncovering underlying issues and identifying areas requiring further examination.
5. Remaining Neutral
Maintaining neutrality during audit interviews is crucial for preserving objectivity and avoiding bias. Auditors should refrain from expressing personal opinions or judgments and focus on gathering factual information based on evidence. Neutral questioning helps in mitigating defensiveness and encourages interviewees to provide honest and forthcoming responses.
6. Empowering Interviewees
Empowering interviewees involves providing them with opportunities to express their perspectives, concerns, and suggestions regarding the audit process. Auditors should create a non-threatening environment that encourages collaboration and participation. Engaging interviewees as active contributors enhances the quality of information obtained and fosters a sense of ownership over audit findings.
Click Here to Download Readymade Editable Toolkits & Templates on Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Lean Six Sigma, Risk Management, Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, HSSE, Project Management etc.
Tools for Enhancing Audit Interviews
1. Interview Guides
Developing interview guides containing predefined questions and topics facilitates consistency and ensures all relevant areas are covered during audit interviews. Interview guides can be tailored to specific audit objectives, processes, or control activities, serving as roadmaps for conducting structured interviews.
2. Audit Software
Utilizing audit management software streamlines the interview process by enabling auditors to schedule interviews, record responses, and document findings in a centralized platform. Audit software often includes features such as customizable interview templates, automated reminders, and real-time collaboration capabilities, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
3. Data Analytics Tools
Incorporating data analytics tools allows auditors to analyze large volumes of data efficiently, identify patterns, and detect anomalies. Data analytics tools can be utilized to validate interview responses, perform trend analysis, and assess the effectiveness of controls. Leveraging data analytics enhances the audit process by providing deeper insights and supporting evidence-based decision-making.
Click Here to Download Readymade Editable Toolkits & Templates on Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Lean Six Sigma, Risk Management, Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, HSSE, Project Management etc.
4. Mind Mapping
Mind mapping tools aid auditors in visually organizing and structuring information obtained during interviews. Auditors can create mind maps to illustrate relationships between different processes, controls, and risks, facilitating comprehensive analysis and identification of interdependencies. Mind mapping enhances communication and assists auditors in presenting complex information in a clear and concise manner.
5. Electronic Surveys
Conducting electronic surveys enables auditors to gather feedback from a large number of stakeholders efficiently. Electronic survey tools allow auditors to design customized questionnaires, distribute them electronically, and analyze responses in real-time. Surveys can be utilized to assess stakeholders' perceptions, evaluate control effectiveness, and identify areas for improvement.
6. Communication Tools
Utilizing communication tools such as video conferencing platforms and collaboration software facilitates remote audit interviews, especially in distributed or global organizations. Communication tools enable auditors to conduct virtual interviews, share documents securely, and maintain ongoing communication with stakeholders. Leveraging communication tools enhances flexibility and accessibility during the audit process.
In conclusion, employing effective techniques and tools is essential for conducting successful audit interviews. By establishing rapport, actively listening, asking open-ended questions, and employing appropriate tools, auditors can gather comprehensive information, assess control effectiveness, and provide valuable insights to stakeholders. Adopting a strategic approach to audit interviews enhances the overall quality and efficiency of the auditing process, ultimately contributing to organizational success and risk management.
Click HERE to download or any of the following process improvement products:
HACCP Implementation Kit
ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems (QMS) Implementation
ISO 22000 Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS) Implementation
Food Safety Systems Certification (FSSC) 22000 v5 Implementation
ISO 14001 Environmental Management Systems (EMS) Implementation
ISO 45001 Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OH&SMS) Implementation
ISO 50001 Energy Management Systems (EnMS) Implementation
Integrated Management Systems (IMS) Implementation
Production, Quality Control / Equipment Maintenance Kit
Lean Six Sigma
Lean Management/Manufacturing
Six Sigma Kit
Supplier Quality and Compliance Management (SQCM) Kit
Risk Management
Industrial Health, Safety & Environmental Management (HSE) Kit
Process Manuals