लीन मैन्यूफैक्चरिंग पहलों के ROI को मापना
Lean manufacturing is a powerful methodology aimed at improving efficiency, reducing waste, and enhancing overall operational performance. However, organizations often face challenges in quantifying the return on investment (ROI) for lean initiatives. Demonstrating ROI is essential for securing executive buy-in, sustaining momentum, and validating the value of lean transformations.
This article outlines the key elements of measuring the ROI of lean manufacturing initiatives, including critical metrics, methodologies, and best practices.
Understanding ROI in Lean Manufacturing
ROI in lean manufacturing refers to the financial and operational benefits gained relative to the cost of implementing lean initiatives. It encompasses tangible outcomes like cost savings and revenue increases, as well as intangible benefits such as improved employee morale and customer satisfaction.
The formula for ROI is typically expressed as:
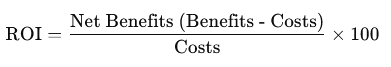
In the context of lean manufacturing, "benefits" and "costs" can include a variety of factors, both quantitative and qualitative.
Key Metrics to Measure ROI
1. Cost Savings
- Material Waste Reduction: Track reductions in material consumption and scrap rates.
- Labor Productivity: Measure output per labor hour or reductions in overtime costs.
- Energy Efficiency: Evaluate reductions in energy consumption and utility costs.
2. Process Improvements
- Cycle Time Reduction: Measure improvements in process cycle times.
- Setup Time Reduction: Assess decreases in the time required to prepare for production.
- Throughput: Monitor the increase in production volume without additional resources.
3. Quality Enhancements
- Defect Rates: Track reductions in the number of defective products.
- Rework and Scrap: Measure decreases in costs associated with rework and scrap.
- Customer Returns: Evaluate declines in returned products or warranty claims.
4. Customer Metrics
- On-Time Delivery: Measure improvements in meeting delivery schedules.
- Customer Satisfaction: Use surveys or Net Promoter Scores (NPS) to assess changes.
5. Financial Metrics
- Revenue Growth: Track increases due to higher throughput and reduced lead times.
- Working Capital: Evaluate improvements in inventory turnover and cash flow.
- Return on Assets (ROA): Monitor how effectively resources are utilized.
Click Here to Join the Over 7000 Students Taking Highly Rated Courses in Manufacturing, Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Project Management, Engineering, Food Safety, Lean Six Sigma, Industrial Safety (HSE), Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, Product Development etc. on UDEMY.
Steps to Measure ROI
1. Define Clear Objectives
Establish specific, measurable goals for lean initiatives. These might include reducing defect rates by 20% or decreasing cycle time by 15%. Clear objectives help align stakeholders and provide benchmarks for evaluation.
2. Baseline Performance
Before implementing lean initiatives, measure current performance. Baseline data provides a point of comparison to evaluate improvements.
3. Track Implementation Costs
Document all expenses related to lean implementation, including:
- Training and development
- Consultant fees
- New tools, software, or equipment
- Time and resources spent on process changes
4. Collect Data Continuously
Use tools such as value stream mapping, KPIs, and statistical process control (SPC) to monitor progress in real-time.
5. Analyze Results
Compare post-implementation performance to baseline metrics to calculate tangible and intangible benefits. Ensure financial impacts are translated into monetary terms for consistency.
6. Adjust for External Factors
Account for market conditions, seasonal variations, or other external influences that may impact results.
7. Report ROI
Present findings to stakeholders in a clear, concise format. Use visual tools like graphs, dashboards, and case studies to highlight key achievements.
Click Here to Join the Over 7000 Students Taking Highly Rated Courses in Manufacturing, Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Project Management, Engineering, Food Safety, Lean Six Sigma, Industrial Safety (HSE), Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, Product Development etc. on UDEMY.
Best Practices for Maximizing ROI
1. Focus on High-Impact Areas
Prioritize lean initiatives that address bottlenecks, high-cost activities, or customer pain points for maximum ROI.
2. Engage Employees
Employee involvement is crucial for sustaining lean transformations. Invest in training and encourage a culture of continuous improvement.
3. Integrate Technology
Leverage digital tools such as IoT sensors, predictive analytics, and automation to enhance lean processes.
4. Monitor Long-Term Gains
ROI measurement should not end after initial implementation. Continuously track performance to identify additional improvement opportunities.
5. Balance Tangible and Intangible Benefits
While tangible benefits are easier to quantify, intangible benefits such as improved morale, better collaboration, and enhanced brand reputation also contribute to long-term success.
Challenges in Measuring ROI
- Data Collection: Accurate data collection can be challenging, especially in legacy systems.
- Intangible Benefits: Converting qualitative improvements into monetary terms is often subjective.
- Time Lag: The benefits of lean initiatives may not be immediately visible, making it harder to link outcomes to specific interventions.
Click Here to Join the Over 7000 Students Taking Highly Rated Courses in Manufacturing, Quality Assurance/Quality Control, Project Management, Engineering, Food Safety, Lean Six Sigma, Industrial Safety (HSE), Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 22000, ISO 45001, FSSC 22000, Product Development etc. on UDEMY.
Case Study: ROI of a Lean Initiative
A mid-sized manufacturing company implemented lean principles to reduce lead times and defects.
- Objective: Reduce lead time by 25% and defect rates by 15%.
- Costs: $150,000 for training, equipment upgrades, and consulting fees.
- Results:
- Lead time decreased by 30%, improving delivery reliability.
- Defect rates dropped by 20%, saving $80,000 annually.
- Inventory levels decreased by 15%, freeing up $50,000 in working capital.
ROI Calculation:
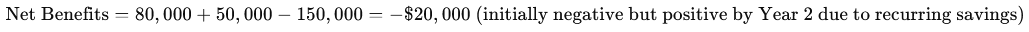
Conclusion
Measuring the ROI of lean manufacturing initiatives requires a systematic approach to tracking costs, benefits, and performance improvements. By focusing on clear objectives, comprehensive data collection, and continuous monitoring, organizations can effectively demonstrate the value of lean transformations. The insights gained from ROI analysis not only validate lean initiatives but also pave the way for sustained operational excellence.
Collection of In-Demand Industry Courses:
1. MANUFACTURING, QUALITY, PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT, OPERATIONS & SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
- Operational Risk Management
- Food Security Management
- Quality Management
- Manufacturing Operational Excellence
- Lean Manufacturing
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
- Essentials of Engineering Project Management
- Construction Project Management
- Essentials of Contract Management
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
- Laboratory Management Systems (LMS) Essentials
- Certified Manager of Quality & Process Excellence
- Essentials of Facility Management
- Agile Project Management
- Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA)
- Engineering Codes, Standards and Specifications
- Industrial Process Safety
- Fundamentals of Risk Management
- Industry 4.0: Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
- Manufacturing Operations Management Certification Course
- Total Quality Management (TQM) Certification Course
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) MasterClass
- Six Sigma for Business and Manufacturing Process Improvement
- Product Management Certification Course
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Data Analysis Course
- Quality Assurance for Business and Operational Excellence
- Essentials of Facility Management
- Agile Project Management
- Engineering Codes, Standards and Specifications
2. ISO MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS IMPLEMENTATION & INTERNAL AUDITOR COURSES
- Integrated Management Systems (IMS) Implementation Course
- FSSC 22000 Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- ISO 22000 Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- ISO 22000 (HACCP, PRPs, oPRPs and CCPs) for Food Safety
- Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) Training Course
- ISO 9001 (QMS) Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- ISO 14001 (EMS) Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- ISO 45001 (OH&SMS) Implementation & Internal Auditor Course
- Food Fraud Mitigation & Defense Certification Course
3. ISO LEAD AUDITOR COURSES
- ISO 50001 Energy Management Systems (EnMS) Lead Auditor Course
- ISO 22000 Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS) Lead Auditor Course
- ISO 14001 Environmental Management Systems (EMS) Lead Auditor Certification Course
- ISO 45001 Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OH&MS) Lead Auditor Certification Course
- ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems (QMS) Lead Auditor Course
- ISO/IEC 17025 – Laboratory Management Systems Certification